Data Diode is a security device for physical one-way data transmission, providing a deployment plan that ensures quality of service, security , and wide deployment capabilities. This article introduces Data Diode solutions and practical applications in militaries of different countries.
About Data Diode solution for safe one-way data transmission
Today, communication technology facilitates the exchange of information between devices and networks. However, it is a common practice in network architecture to add protective barriers between trusted and untrusted networks. In the US Industrial Automation and Control System (IACS) guidelines, many protective barrier devices are proposed between a power plant control network and unsafe networks. (such as factory networks and the internet (NIST, 2011)). The report of the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has listed the threats to the industrial network control system (ICS), sorted by the level of decreasing risk, Specifically: software containing malicious code (38%), system not updated with patches (29%), open connections (17%), regulatory violations (9%), finally leaking information, exploiting and opening backdoors. Corresponding to the above threats, DHS also recommends 7 strategies to protect Critical Industrial Infrastructure. According to statistics in 2014-2015, these strategies help prevent attacks on the system up to 98%. Some of those strategies are:
1. Applications are confirmed (Application Whitelisting): up a list of applications that are allowed to be installed.
2. Establish standard configuration policy and validated patch update schedule.
3. Minimize the scope to be protected, such as isolating the ICS system, blocking unused services/ports; use Data Diode to divide functional network areas; For networks that need bidirectional data transmission, use each port separately for each data transmission/receiving line.
4. Build a protected environment: restrict direct paths between servers; prevent and prevent infection.
5. Ensure secure remote access: Find and remove backdoor and modem access applications; only allowing monitoring to be performed by the Data Diode hardware device and not by software with a “read-only” configuration setting; grant connection permission per session with time setting, do not grant connection permission permanently.
From the above options, it shows that there are two approaches in implementing the IACS system security.
Firstly , the strategy is based on building an explicit policy to ensure system safety such as: unifying secure applications installed on the system; coordinate with the OS/software vendor to request official patches from the manufacturer; lock unused ports/services on the system, control/monitor device access, limit persistent remote connections.
Second , DHS proposes a new technology-oriented security device, named Data Diode . This is a secure device for physical one-way data transmission, providing a deployment option that ensures quality of service, security, is widely deployable, and has been proven to be reliable and reliable. extensible in many government agencies.
The problem is that industrial networks with sensitive and important data need to be isolated, but still have a policy of decentralization of access with authorized users, easily leading to the risk of being hacked. network public. The best solution is to apply advanced technology, the Data Diode security device only allows one-way information flow, which is invulnerable to network attacks.
In fact, Data Diode is most commonly used in IACS systems, bank data centers and military systems. This solution is implemented according to 2 main models, to preserve the basic properties of a system.
-
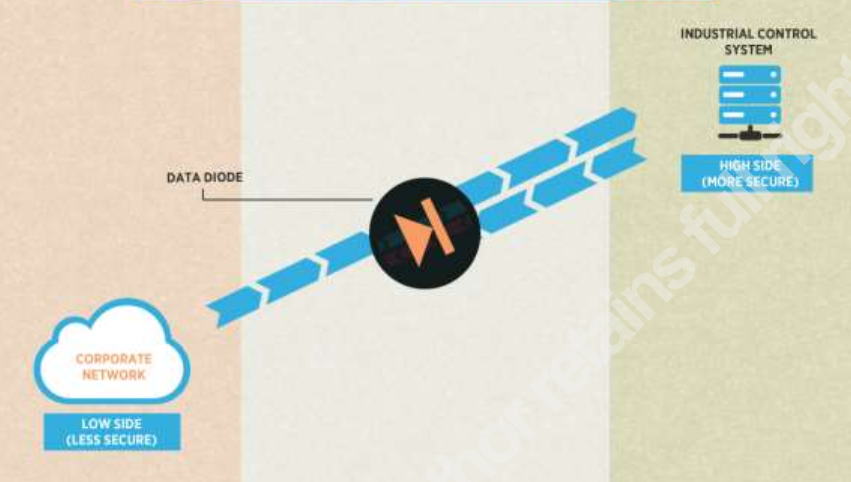
Figure 1. System model Data-only system – highly secure configuration [1]
The system only receives data – high security configuration (Receive – Only – High-Confidentiality Configuration) preserves the security of the system. In the protected state, the system will only receive data from other systems, without any data being transmitted in the opposite direction. Attacks or exploits can be sent to the protected network. However, no information about this network can be sent back to the outside network.
Transmit – Only – High -Availability Configuration (Transmit – Only – High -Availability Configuration) system preserves system availability. In the protected state, the system will only transmit data to other systems, without receiving any data from other systems.
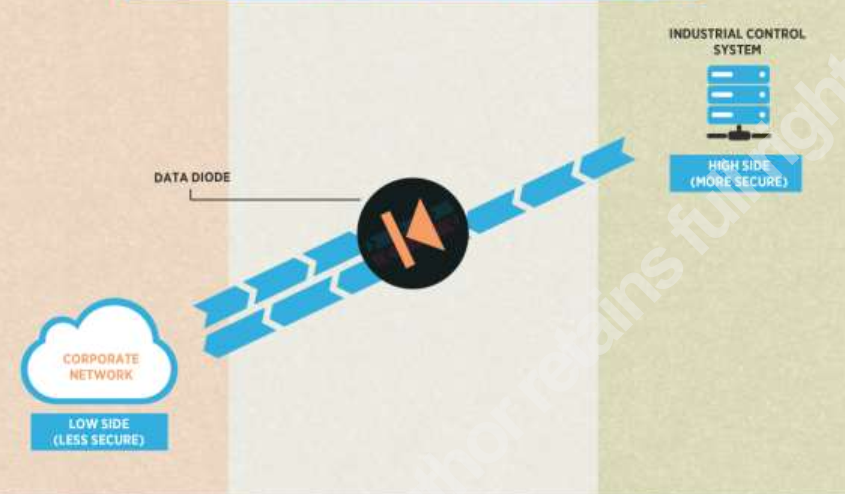
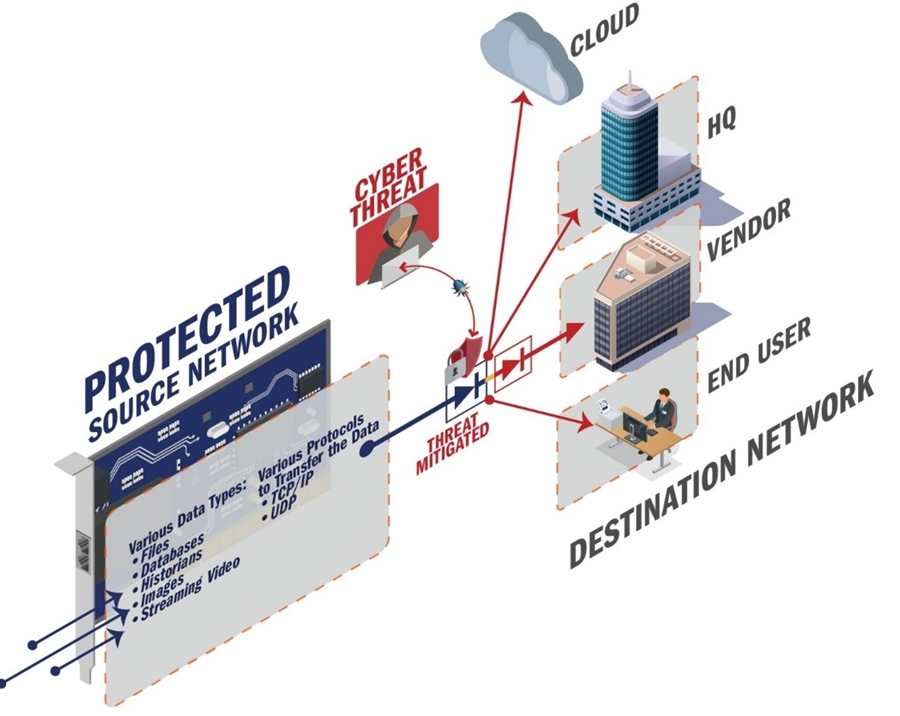
Figure 2. Play-only system model – high availability configuration [1, 2]
Because of this feature, the system only broadcasts – the available configuration is capable of: The protected network cannot be remotely scanned, attacked or hijacked; resistant to denial of service attacks.
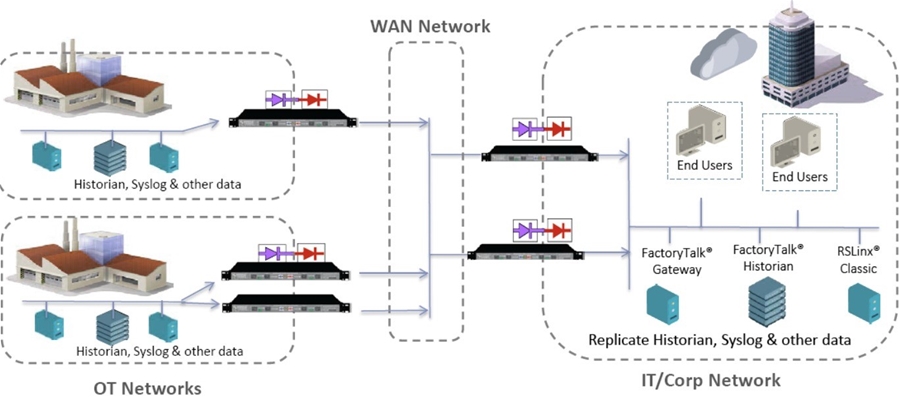
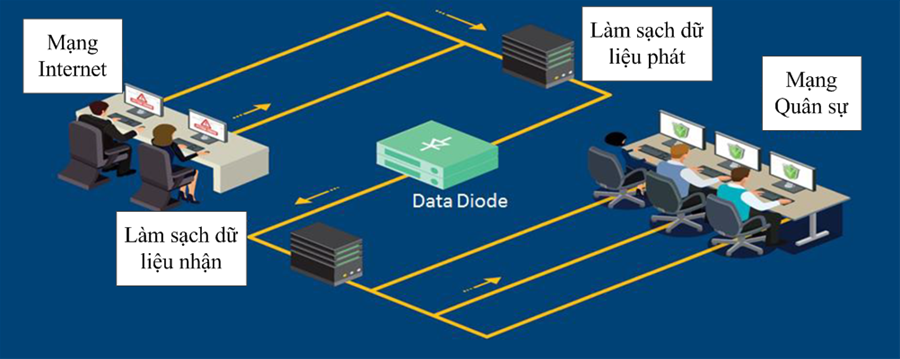
Figure 3: Model of data transmission security system using Data Diode one-way data transmission device.
Compare Data Diode and Firewall
Firewalls are a common edge-layer security technology. Firewalls operate dynamically based on rule sets (Forrest, 2012). Because they are software-based, firewalls are vulnerable to security vulnerabilities such as configuration errors and backdoor malware infections, leading to potentially vulnerable networks (Kamara, 2001). . Data Diode is an edge layer security technology that has been shown to completely eliminate the disadvantages of firewall technology (Westmacott, 2003). However, this technology is not yet widely applied. Data Diode works on a single principle that data will only flow in one direction between networks.

The first, Data Diode ensures secure separation of networks. Network segregation is one of the most effective ways to protect the network. This method makes it very difficult for hackers to gain access to components of the network. In this way, access to sensitive information or critical systems can be effectively limited. Methods for network segregation include physical isolation, traffic flow filters, creation of VLANs, use of proxies, and most widely known as firewalls. All of these methods can be part of a secure network architecture. But among the above methods, none can provide absolute certainty that the network cannot be hacked and that the data will only travel in one direction. Data Diode is the only security solution that can guarantee that data is transmitted in one direction. The Data Diode device is physically simple and includes only fiber ports and power connections. The physical link for optical signals and electrical signals (which make up data) is only allowed for transmission in one direction. The Data Diode does not contain any software or other logic gates, so configuration errors or attacks are unlikely.
Second , Data Diode has lower cost and reduced complexity compared to firewalls and other software solutions. Besides, Data Diode has low maintenance cost. The Data Diode device does not physically need to be updated. The configuration of the diode is simple, does not require professional people to maintain. The use of Data Diode reduces the complexity of the network. It doesn’t matter if a configuration error exists, an administrator can be absolutely certain that data can only flow in one direction.
Third , Data Diode enables real-time data transmission in highly secure environments. The solution to segregate networks in highly secure environments (e.g. nuclear power plants or highly secure agencies) has long been deployed to physically isolate the network. This solution is no longer viable. Nowadays, the amount of data is increasing day by day. This requires being able to process and react to data as quickly as possible. From these trends, there is no possibility to transfer data from one network to another using CD or USB. These mission-critical environments can now securely transmit large amounts of live data at high speeds through a Data Diode.
Fourth , Data Diode has the ability to prevent physical damage. In industrial networks, digital systems are connected to physical processes. These are also referred to as physical network systems. When these systems are connected to unsecured networks (the Internet), this will create conditions for hackers to gain control leading to data leakage. By using Data Diode, data can be shared from the industrial network to the office network without worrying about hackers breaking into the physical network.
Fifth , propose internal regulations or force the implementation of Data Diode. Some countries have proposed or even mandated specific organizations (mainly those in government or critical infrastructure industries) to implement Data Diode in their networks.







